
BLOG
KATEGORİDEKİ DİĞER YAZILAR
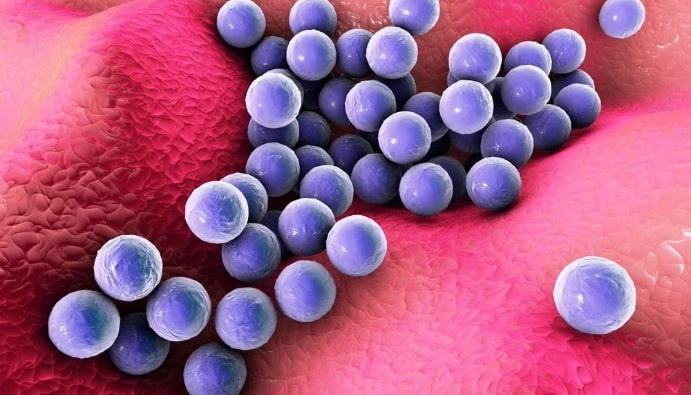
Staphylococci are pathogens for humans and other mammals. They are typically gram-positive, unicellular, paired or more often found in clusters resembling a bunch of grapes. The genus name Staphylococcus is derived from the Greek words “staphyle and kokkos”, meaning “a bunch of grapes”. Staphylococci are widespread in nature and are found on the skin and mucous membranes of mammals and birds.
Pathogenic Staphylococci are bacteria, usually of the genus Staphylococcus, that can cause various health problems. These bacteria can cause infections in both humans and animals. The most common types are Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus saprophyticus. damage that pathogens can cause:
Pyoderma (Superficial Skin Infections): It can cause skin problems such as acne, impetigo (skin crusting), and furuncles (pimple-like abscesses).
Severe Skin Infections: It can cause extensive skin infections and abscesses.
Mastitis Mastitis (inflammation of the udder) can develop, especially in lactating animals. Staphylococcus aureus is a common cause of mastitis and can lead to reduced milk yield and pain in the breast tissue.
Cellulitis: A common infection of the soft tissues under the skin.
Abscesses: It can cause inflamed bumps under the skin.
Osteomyelitis: An infection of the bone that can cause pain, swelling and fever.
Septic Arthritis: It can cause joint infections, leading to pain and limitation of movement.
Septicemia (blood poisoning): Occurs when bacteria enter the bloodstream and can lead to organ failure, high fever and serious health problems.
Endocarditis: It is an infection of the heart valves and can cause serious heart disease.
Staphylococcal Enterotoxin: Caused by toxins produced in food products. It can cause symptoms such as severe nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
MRSA (Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus): MRSA is resistant to methicillin and other antibiotics and is common in hospital settings. It can cause infections in surgical wounds and other medical devices.
Effects on the Immune System: Pathogenic Staphylococci can lead to more serious infections in individuals with compromised immune systems (e.g. diabetes, HIV/AIDS).
Staphylococci pathogens in medical devices can pose various infection risks and can lead to serious health problems in hospital settings.
Failure to comply with hygiene rules in production areas and ignoring personnel hygiene is unacceptable.
For all your questions about the Determination of Pathogenic Staphylococci in Medical Devices, you can contact our expert and authorized team as Nanolab Laboratories Group. We also provide services on In Vivo Tests, you can visit our website for detailed information.
For more information visit our website: https://www.nano-lab.com.tr/
You can follow us on LinkedIn for up-to-date news and posts about our services.
Follow our Instagram account to be informed about our latest blog posts.