
BLOG
KATEGORİDEKİ DİĞER YAZILAR
Edible fats and oils are essential for nutrition. However, edible fats and oils carry the risk of oxidation or acidification in foods. In cases of oxidation or acidification, the quality of food decreases. This can cause health problems. Currently, one of the best ways to prevent oxidation in edible fats and oils is the addition of antioxidants.
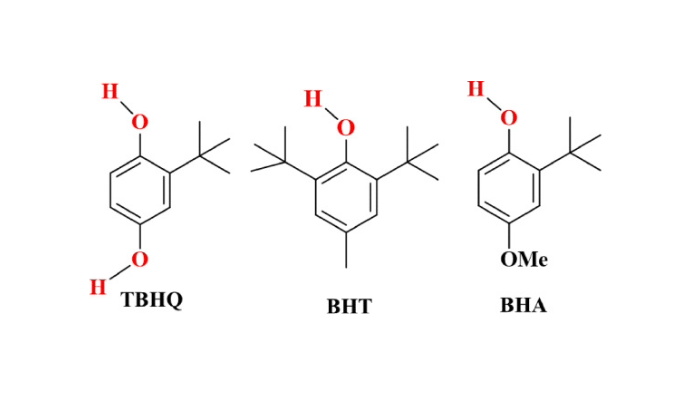
Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA), tert-butylhydroquinone (TBHQ) are antioxidants commonly used in edible fats and oils.
According to their antioxidant potential, they can be ranked as follows: BHT > BHA ≈ TBHQ
BHT, BHA, TBHQ antioxidants can be found in many foodstuffs. The highest value determined for other antioxidants within the scope ofthe Turkish Food Codex Communiqué on Food Additives Other Than Colorants and Sweeteners is as follows.
The highest limits for antioxidants coded E 319 Reversible butyl hydroquinone (TBHQ), E 320 Butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA), E 321 Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT):
Nanolab Laboratories Group continues to provide services within the scope of Antioxidant (BHT, BHA, TBHQ) Determination in Foods. We also provide services for determination of additives in foods.
Contact us for more information.
You can follow us on LinkedIn for up-to-date news and posts about our services.
Follow our Instagram account to be informed about our latest blog posts.