
BLOG
KATEGORİDEKİ DİĞER YAZILAR
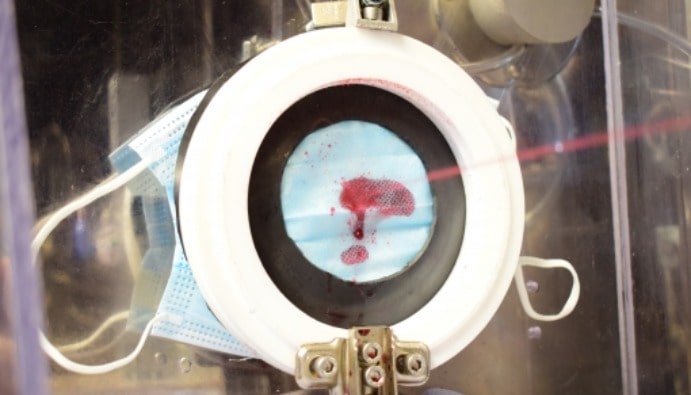
Medical masks, especially used by healthcare workers, are designed to provide protection against droplets carrying blood, body fluids or other microorganisms. Therefore, the mask is expected to be resistant to splashes of liquids. The splash resistance pressure test is a test that measures the mask's ability to block liquids and aerosols from passing from the outside to the inside.
The purpose of the test is to measure the mask's level of resistance to liquid splashes, helping to protect users, especially in surgical environments where liquids come into direct contact. These resistance levels of masks are of great importance for healthcare workers and patients, as splashes are a major risk factor in the spread of infections.
The splash resistance test performed on medical masks is a test performed to determine the resistance of the mask against blood-borne pathogens. In the splash resistance test method, high velocity constant volume synthetic blood is splashed into the center of the mask to determine whether the mask acts as a barrier.
Applicable standards with international validity when performing splash resistance tests on medical masks:
The splash resistance pressure test is a test performed under a specific liquid and pressure. This test is performed by splashing liquid on the outer surface of the mask and evaluating whether there is liquid passage to the inside of the mask. The basic steps of the relevant test are as follows:
Nanolab Laboratories Group continues to provide services within the scope of Medical Device Analysis.
Contact us for more information.
You can follow us on LinkedIn for up-to-date news and posts about our services.
Follow our Instagram account to be informed about our latest blog posts.